Cancer prevention
Find out the most common symptoms of cancer and what to do if you experience them.

What is cancer?
You can imagine cancer as an “out of control” cell multiplication, which can occur in any organ of your body.
This affected organ can then grow and push other organs out of their location or even lose its function.
Tumors
Depending on the severity, we talk about:
- Benign tumors – with clear borders, they don't spread across the body.
- Malignant tumors – they spread across the body by blood and lymphatic system and form other tumors (metastasis).
How does cancer manifest itself?
Cancer can have symptoms, but it doesn't necessarily have to - it can be asymptomatic for a long period of time. The symptoms can be divided into “general symptoms” and “specific symptoms”, depending on the type and location of cancer:
General symptoms:
-
Weight loss
-
Nausea, vomiting
-
Lumps
-
Pain
-
Loss of appetite
Specific symptoms:
-
Jaundice – liver, pancreas and gallbladder cancer
-
Bleeding – from nose, cervix, rectum
-
Defects of vision, headaches – brain cancer
-
Diarrhea / constipation – colon cancer
-
Cough – lung cancer
-
Fractures – bone cancer
Prostate
Prostate can be easily described as a “gas station for sperm”. This organ provides sperm with energy and nutrients needed in their long and exhausting run towards egg fertilization.
Prostate disease symptoms
Prostate cancer is often asymptomatic for a long period of time. When the cancer spreads, the symptoms are similar to benign enlargement. The prostate can push the urinary bladder and urethra from below and this can result in following symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating
-
Intermittent urinating
-
Frequent urination
-
Painful urination
-
- Blood in urine
Testicles
Testicles, testes or balls if you wish are responsible for the production of testosterone - the male sex hormone. Apart from that, male reproductive cells - sperms - are “born and raised” here, in temperatures lower by 4°C from the rest of the body.
Testicular fun facts:
- 20 grams - that's how heavy one testis is.
- 15 millions sperm per milliliter of semen.
- 72 days to develop a fully mature sperm.
How does testicular cancer manifest itself?
How does testicular cancer manifest itself?
-
Lump
-
Enlargement
-
Swelling
-
Pain
Uterus and ovaries
Ovaries are mainly responsible for the production of female sex hormones - estrogens and progesterones. Apart from that, ovaries serve as a reservoir for female sex cells - eggs. If the eggs are fertilized, they implant into the thickened walls of the uterus, which then serves as a small “incubator” for babies.
How does cancer of women genital area manifest itself?
How does cancer of women genital area manifest itself?
-
Bleeding after menopause
-
Irregular periods
-
Bloody discharge
Cervix
Cervix can be described as a “plug” protecting the uterus from an infection, which can develop in a vagina. At the same time, it secures the baby at its place for the whole 9 months, creating a safe space for its development.
Cervix cancer is predominantly caused by human papillomavirus (HPV 16 or 18). This virus transforms healthy cells into cancerous ones and can also be responsible for genital herpes type 6 or 11.
How does cervical cancer manifest itself?
-
Bloody discharge
-
Bleeding after sex
-
Lower abdominal pain
Breasts
Breasts, also known as boobs, are mainly responsible for the production of breast milk. However, we can't deny their aesthetic and seductive function.
Breasts - fun facts:
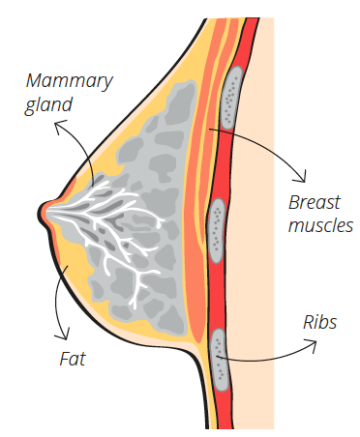
- D average size of breasts in Czech Republic.
- 500 grams - the weight of one average breast.
- 67 kilocalories - per 100 millilitres of breast milk - which is more than one beer.
How does breast cancer manifest itself?
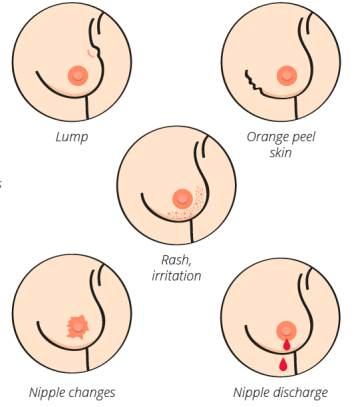
-
Lump
-
Orange peel skin
-
Rash, irritation
-
Nipple changes
-
Nipple discharge
Every woman after 45 should undergo mammography every 2 years. See the list of mammography centers at www.mamo.cz.
Large intestine
The large intestine is responsible for water absorption and production of vitamin K.
Large intestine - facts:
-
Colon cancer is the 3rd most common type of cancer in the Czech Republic.
-
The large intestine is 1.5 meters long.
-
Only 35 % of people above 50 go to regular colon cancer screenings.
Colon cancer symptoms:
-
Weight loss
-
Diarrhea
-
Constipation
-
Rectal bleeding (Fecal Occult Bleeding)
How to prevent colon cancer?
-
Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables - it has a lot of fiber to clean your colon.
-
Reduce consumption of red meat and alcohol - it can harm the cells in your colon.
-
Go to regular check-ups to your general practitioner - to prevent fecal occult bleeding.
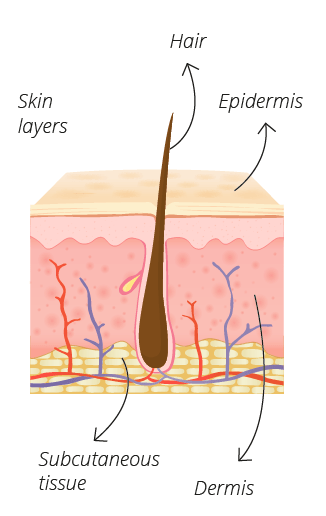
Skin
Skin is the largest organ of your body. It protects you from cold, various infections and last but not least UV radiation. It also serves a major role in production of vitamin D.
Skin (fun) facts:
- it takes a surface of about 1,7 m²
- 8 % of body weight is skin
- it weighs about 5kg on average (depending on the amount of fat)
- skin cancer is the most common type of cancer
- in men, melanoma most often occurs on the trunk
- in women, melanoma most often occurs on the shins and calves or on the back
- 30 to 50% of melanomas manifest from an existing birthmark
- safe sunbathing does not exist; tanning beds will not give you a better “base” for sunbathing
What is UVA and UVB radiation?
You probably already heard about an ultraviolet radiation. It is the “problematic” part of sun radiation which can cause skin or eye damage. The intensity of sunlight increases by approximately 4% with every 300 m above sea level.
O ultrafialovém záření jsi už určitě někdy slyšel/a. Jde o “problémovou” část slunečního záření, které může způsobovat poškození lidské kůže a očí. Intenzita slunečního světla se zvyšuje přibližně o 4 % s každými 300 m nadmořské výšky. The main long-term effects of sunlight are skin aging (photoaging) and the formation of tumors (photocarcinogenesis)
Ultraviolet radiation consists of UVA (95 %) and UVB (5 %) radiation:
UVA radiation:
- is stronger in the morning and in the evening
- damages the deep layers of skin
- causes skin aging (wrinkles)
UVB radiation:
- is strongest between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m.
- it tans and causes skin to get red
UV index:
- Indicates the amount of negative effect of UV rays on the skin, which causes redness.
What material (does not) pass UV radiation?
Sunlight can reach you even in the shade. You must take into account the nature of your surroundings: white sand, fresh snow, water surface or white concrete surfaces reflect sunlight.
And what about glass? Ordinary glass in window panels or cars passes light and UVA radiation very well.
Apart from sun lotions, you can protect yourself even with your clothing. The efficiency depends on the material - its color, thickness, type, size and elasticity. Colored and black clothes protect more, however they absorb more light than white clothes and therefore become uncomfortably hot. You should also carry your sunglasses with a certified UV filter with you.
How can skin get sick?
You can imagine cancer as an “out of control” cell multiplication, which can occur in any organ of your body. This affected organ can then grow and push other organs out of their location or even lose its function. Even skin can be affected by cancer. What are the most common types?
- Basal cell carcinoma: this type of skin cancer is the most common and its rate has doubled in the last 15 years. In 80% of cases, it occurs on the head and neck.
- Melanoma: is a malignant cancer of pigment cells, occurring predominantly on the skin, however, it can also occur under a nail or in the eye.
Skin cancer symptoms
Skin cancer can be easily recognized by certain changes in your birthmarks. Do this self check - up once a month to detect them. If you answer “yes” to at least one of the questions above, go to your doctor:
Metod ABCDE
A - Asymmetry
Is your birthmark asymmetrical?
B - Border
Does your birthmark have no apparent borders?
C - Color
Is there a sudden change of color?
Is the diameter of your birthmark bigger than 0,6 cm?
Can you spot any evolution or other changes in your birthmark?
Skin cancer risk factors:
- age above 50
- melanoma history in family
- UV radiation
- sensibility to sun exposure
- increased excessive exposure to sunlight in childhood, sunburning into blisters in childhood, bullous dermatitis after sunburn in childhood
- tanning beds
- increased number of atypical freckles or large freckles (bigger than 20 cm in adulthood)
- changing pigment spots
- immunosuppression (e.q., during HIV infection)
How to prevent skin cancer?
- Stay away from the sun between 11 a.m. to 3 p.m. At noon, the intensity of UV radiation is twice as high as at 10 a.m. or 4 p.m.
- Wear suitable clothing and glasses with a certified UV filter.
- Use sunscreen every 2 hours (with a high factor - preferably 50+, which passes only 1/50 of ultraviolet radiation into the skin). Use enough sunscreen - even about 30 grams (6 tea spoons) for an adult body.
- Protect your children - frequent sunburns in childhood can increase the risk of skin cancer in adulthood.
- Avoid tanning beds - the main radiation of their lamps is UVA, which causes skin aging.
Is anything still unclear or do you simply have a question?
Donate to Loono
Your donation helps us to buy new models, print leaflets and pay our lecturers and administrative workers for their work.

