Atherosclerosis
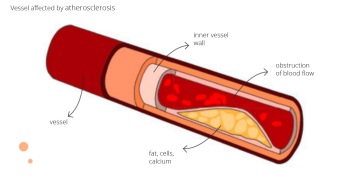
Also called hardening of the arteries is a process in which fat, other cells and calcium build up in the walls of blood vessels. It develops as chronic inflammation. It primarily affects large and medium blood vessels - heart vessels, aorta, common carotid artery, and brain arteries.
What makes atherosclerosis dangerous?
Atherosclerosis plaque is made within the process, and this plaque persistently grows and narrows the blood vessels. If this plaque is ruptured, a clot is created there, which can cause complete closure of the blood vessel. Physically it manifests as a heart attack or a stroke.
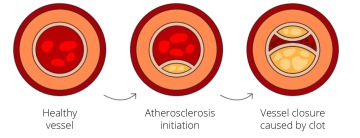
Stages of atherosclerosis
At the age of 10, fatty streaks in the walls of blood vessels may be found - the first stage of this disease. Plaque builds up in these walls over time. Plaque can gradually build up to a state in which the artery is fully clogged. An unhealthy diet, stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, and insufficient physical activity support the growth of this plaque.
What are the symptoms?
At first, the process is painless. Pain doesn't occur until the blood flow is significantly reduced. The blood can't be transported to organs and can cause temporary or permanent damage.
Usually and unfortunately, the first symptoms of atherosclerosis are heart diseases - heart attack, angina pectoris or stroke.
How to prevent an atherosclerosis?
Preventable risk factors:
- Smoking - If you quit smoking, the risk of having a heart attack or stroke lowers by up to 50%.
- Lack of exercise - Exercise regularly, at least 5 times a week for 30 minutes.
- Sleep - Sleep for at least 7 hours a day and go to bed (and from it) at the same time every day (yes, even at weekends :) )
- Diabetes - If you have diabetes, get checked by your doctor regularly
- Blood pressure - If you have high blood pressure, check it regularly and take your pills
Non-preventable risk factors:

- Gender - Men are more prone to both heart attack and stroke, women are more protected thanks to their sex hormones - estrogens.
- Age - The risk of having a stroke or a heart attack is higher after you turn 55.
- Genetics - If someone from your family had a stroke before the age of 55, tell that to your GP. Familial hypercholesterolemia, for example, is a hereditary disease, which can manifest at a young age.
FAQs
What to do when...
5 important steps to do when you have or see someone else having a heart attack or stroke.
- Don't panic, don't look for advice on the internet and start acting!
- Call 155 for help!
- Stay where you are and wait for an ambulance
- Is the patient conscious? Shoothe him/her. Check breathing and reactions (talk, pinch the patient's ear)
- Is the patient unconscious? Check breathing - tilt the patient's head back and see, if the chest is moving up and down. If the patient is not breathing, start chest compressions immediately!
What are the most common risk factors?
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Unhealthy diet high in fat
Is it true that smoking is harmful to health?
Yes, of course. Smoking:
- increases the risk of blood clots
- disrupts platelets' function
- increases the number of white blood cells
- reactive oxygen species are being produced and further damage the surface of blood vessels

